|
|
|
|
Soleniod Valve Technology£º
|
| 1. Definition and Operation principle of solenoid valve £º |
| Solenoid Valve is the electron component, actuator that control the fluid, normally control the direction, flow rate etc. |
| 2. Solenoid category and principle: |
a. Linear solenoid valve£º
When power supply energized, the plunger is pulled away the valve seat, open the valve; when power supply deenergized, plunger returned by spring, close the valve. They are grouped into three types: Flexbilitily close valve, Rigiditily close valve, Gap strut type valve. details please refer to below picture:
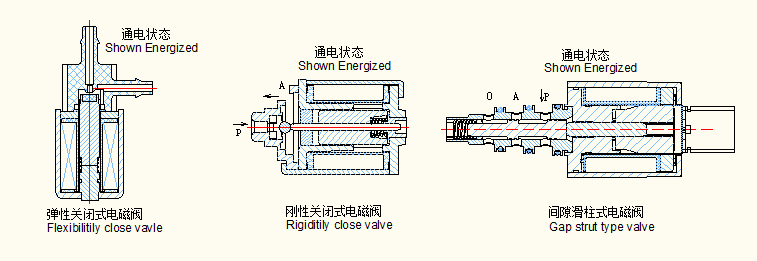 |
| b.Pilot valve: When power supply energized, the pilot hole is opened, the pressure upper room is decreased rapidly, the pressure of the under room is higher than upper room, open the piston, open the valve. When power supply deenergized, the spring close the pilot hole. the pressure of upper room increased again, the upper room pressure is bigger than under room pressure, close the piston, colse the valve. please see below left picture. |
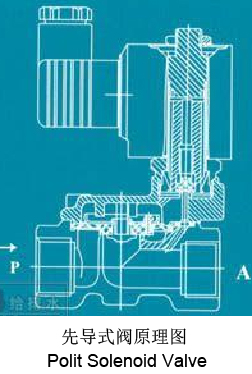 
|
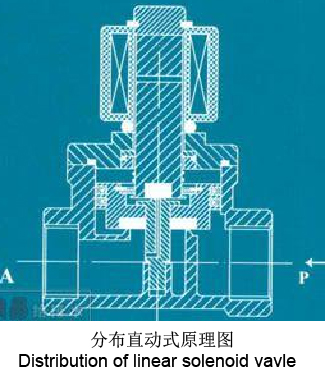
| c.Distribution fo linear solenoid valve£ºIt is integrated from linear valve and pilot valve. when there is no differential pressure between inlet and outlet, after energized, solenoid pull the small polot valve and main valve plunger in turn. open the valve; when there is some differential pressure between inlet and outlet, after energized, solenoid pull the polit valve first, then push the plunger by the differential pressure, after power off, polit valve closed by spring, and push the plunger close the valve. |
| d. Our main valve is linear solenoid valve.
|
| 3. Solenoid valve's selection factors£º |
| Normally select solenoid valve according to :Drift diameter, Connection type, fluid material, fluid temperature, fluid state, fluid viscosity, fluid pressure, voltage, flow rate, operation type(NC or NO), work conditions etc.
|
| 4. Application conditions & requirements form: |
| |
| 5. Pressure unit conversion table £º
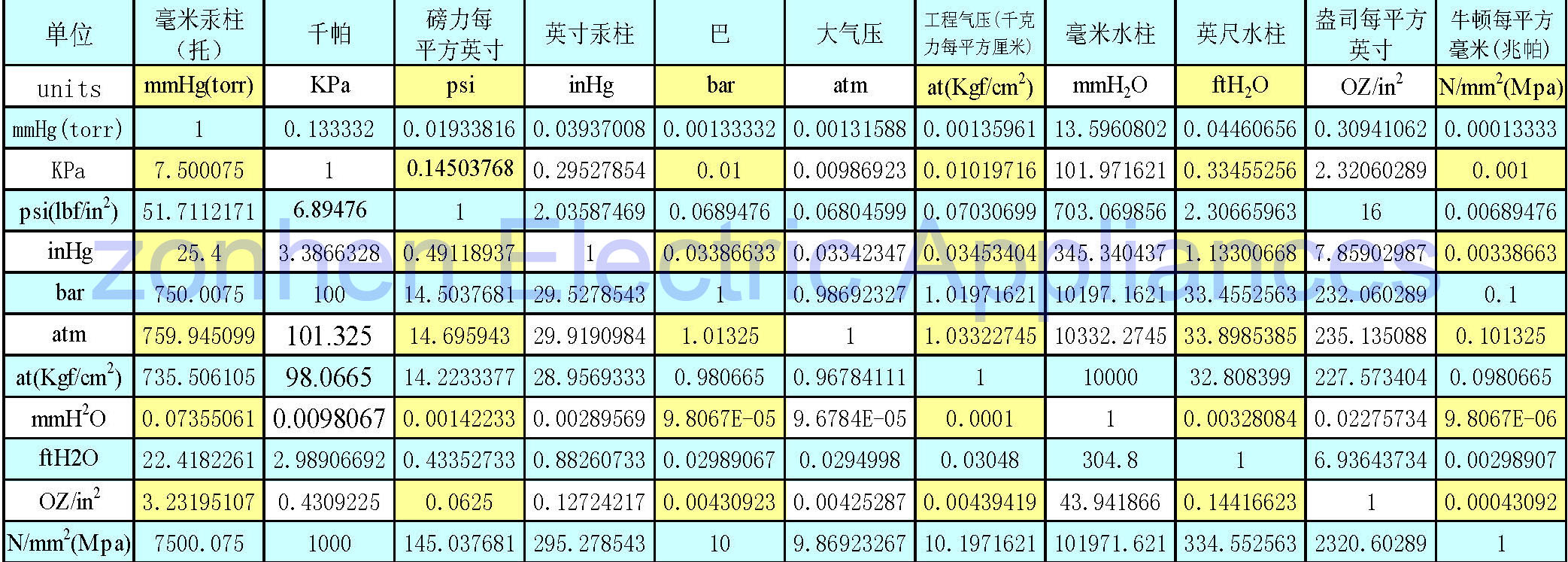
More conversion table |
|




